PCB thickness is critical to the longevity of electronic gadgets. It usually changes how strong your gadget is. Besides, you can determine how flexible and well it can dissipate heat. As you can see, knowing more about Common PCB Thickness is crucial.
Common PCB Thickness Categories
We use hundreds of electronic gadgets every day. You know, not all of them need the same functionality. Each gadget is meant for different tasks in different environments. Because of this, you will need various types of circuit boards. Consequentially, varieties of PCB thickness appear.
Thin PCBs (0.4mm to 1mm)
Thin PCBs are small and lightweight. Therefore, you usually come in small sizes and are perfect for portable devices. People mostly use them on smartphones, laptops, and wearable techs.
Thin PCBs are very flexible and easy to fit into tight spaces. The problem is that thin PCB may not offer a long-lasting service lifespan. However, people prefer these circuit boards for devices where space and weight are primary concerns.
Thicker PCB (1.6mm to 2.4mm)
Thicker PCBs, on the other hand, are the standard choice for most applications. In general, people prefer 1.6mm PCB. It typically balances everything an electronic device needs for better performance.
Extremely Thick PCB (2.4mm to 10.16mm)
As the name suggests, these PCBs are extremely thick and used only for specific applications. From the previous point, you know that the thicker the PCB is, the more current it can flow. So, extremely thick PCBs are used where high current and voltage are necessary, like in heavy-duty applications. You can find them in mining vehicles and power equipment.
What Affects the PCB Thickness?
You may wonder why making such diverse ranges of PCB thickness is necessary. The best answer in this case could be suitability. Does the PCB suit your project needs? Can it endure the environmental conditions? Is it cost-effective and durable?
Factor #1 Number of Layers
The more layers a circuit board has, the thicker it becomes. Each extra layer adds copper and insulation. These changes in PCB layers increase the overall PCB thickness.
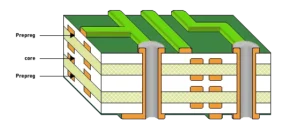
Factor #2 Core and Prepreg Thickness
The core and prepreg are crucial parts of PCBs. The core is made of fiberglass reinforced with epoxy layers and copper on both sides. Prepreg is an adhesive-like layer typically made of fiberglass and resin. The difference between them is their flexibility. The core is generally more rigid, while the prepreg is flexible. Their thickness heavily determines the PCB’s final strength and thickness.
Factor #3 Material Type
The material you use to make a PCB also affects its thickness. In general, people use FR4, polyimide, or metal. Each material has a different thickness size. For example, a typical FR4 PCB is 62 mils or 1.57 mm thick.
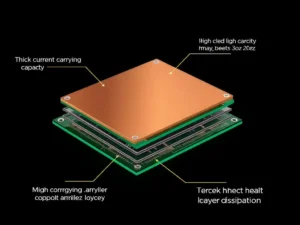
Factor #4 Copper Thickness
Copper layers on the PCB can be thicker or thinner, affecting the platform’s general thickness. This is usually common in high current or high power applications, not forgetting that power is equivalent to current multiplied by voltage.
Factor #5 Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process also affects the thickness of the final produced PCB. The drilling equipment’s ability may define the PCB’s minimal/ maximal thickness level. On the other hand, the method used to separate PCBs from the panel also affects the thickness tolerances.
Common PCB thickness
PCB thicknesses may differ, but specific standard thicknesses are offered for general use, as shown below. The following table enlists typical PCB thicknesses in diverse industries and applications.
| Type | PCB Thickness in mils | PCB Thickness in mm |
| FR4 Circuit Board | 62mils | 1.57mm (widely recognized as 1.6mm) |
| Single Layer Flex | 4mils | 0.11mm |
| Double Layer Flex | 8mils | 0.195mm |
| Semi-Flex | 8mils | 0.2mm |
| Thick Copper | 93mils | 2.4mm |