With the increasing improvement of communication technology and computer technology, electronic information technology has also developed rapidly. In addition to portable electronic products such as mobile phones and laptops used in our daily lives. The use of electronic equipment in automobiles and aerospace is also increasing. Among them the printed circuit board is a very important electronic component. It is the support of the electronic components and the carrier for the interconnection of the electronic components. Therefore, it is very necessary to understand the basic structure of the printed circuit board.
How to choose circuit board components
Deciding which PCB assembly to use can be a daunting task, because there are many different options to choose from. From deciding on the footprint of the component to checking the spare gate. It needs to carefully consider several different factors before deciding which printed circuit board component to use. Here, we provide some tips or suggestions that you may need to consider before deciding which PCB component to choose for your business.
Consider component footprint
- Here, we are referring to the layout stage. At this stage you will need to consider the land pattern and space occupied by the decision. In fact, you should consider the issue of component occupancy during the entire schematic drawing stage. You should also note that the coverage area should include the mechanical components of the involved parts and the electrical pad connections. In other words, it will involve the pins and the body contours of the components that are fixed to the printed circuit board.Therefore, when deciding which component to choose, you should consider any packaging or enclosure restrictions that you may encounter when evaluating the bottom and top of the final printed circuit board.
For example, polarized capacitors and other such components often have a high degree of clearance limitation. Therefore, you must consider as part of the unit selection process. It may be necessary to draw basic circuit board outline shapes when starting to design the layout. Then use it to place the connectors or other such critically placed components. In this way, you can create a virtual rendering of the PCB, which is fast and does not require any wiring. Then it can use the resulting visualization to create components, and extremely accurate visual representations of the height and relative position of the board. In this way, once assembled the printed circuit board, ensure that all the parts involved (such as the mechanical frame, chassis and plastic) are packed in the packaging.
Prepare for change
- Through a variety of different designs, the choice of components may change. The design process is continuously changing. And you should consider which components will use surface plating technology and will plate which components through through holes. By taking the route to pre-select, simplify the entire planning process of the printed circuit board can. Before deciding which printed circuit board components to use, It must to consider carefully the power consumption, component area density, component cost and availability.
Generally speaking, surface mount technology components are easier to access and obtain than their plated through-hole component counterparts. In addition, at least from a manufacturing point of view. They also tend to be cheaper when compare with their plated through-hole component brethren.Interestingly, for medium and small prototyping tasks, recommend that use larger through-hole parts or surface mount technology components for better access to signals and pads during debugging and troubleshooting tasks, and also can simplify them to Manual welding process. It is also important to note that if you cannot get a specific footprint in the database. You can design a custom footprint from the tool.
Implement good grounding practices
- The design you include should have a sufficient number of ground planes and bypass capacitors. If you use an IC, you should make sure to use an appropriate number of decoupling capacitors. When it near the ground plane or other such location power source.Obviously, the capacitor size you choose will largely depend on the frequency involved. And implement the type of capacitor technology and application. In short, it is very important to follow good grounding specifications. Because this will give your printed circuit board optimized magnetization performance and excellent electromagnetic compatibility.
Properly allocate virtual part footprints
- Strongly recommend that you run the bill of materials or BOM to check if there are any virtual components. When find that there are no packages associated with virtual components, and do not need to transferr them to the layout stage In the actual process. By creating a bill of materials, you will be able to evaluate all virtual parts in the design. In terms of input, you should only input ground and power signals. Because they are actually virtual components that the system specifically handle it in a schematic environment rather than a layout environment. In summary, it is necessary that always use components actually to replace the components have a footprint found in virtual parts . Unless only use they for simulation reasons.
The Circuit Board Components
The printed circuit board has many different types, which are used to control and regulate the current through a particular circuit. The most commonly used components in electronic equipment include resistors, capacitors, diodes, transistors, and integrated circuits (IC). Insulators and other tiny electronic components are also mounted on the circuit board. It must place these components on the surface of the printed circuit board (PCB). Only a strategic position can form a useful electronic circuit.
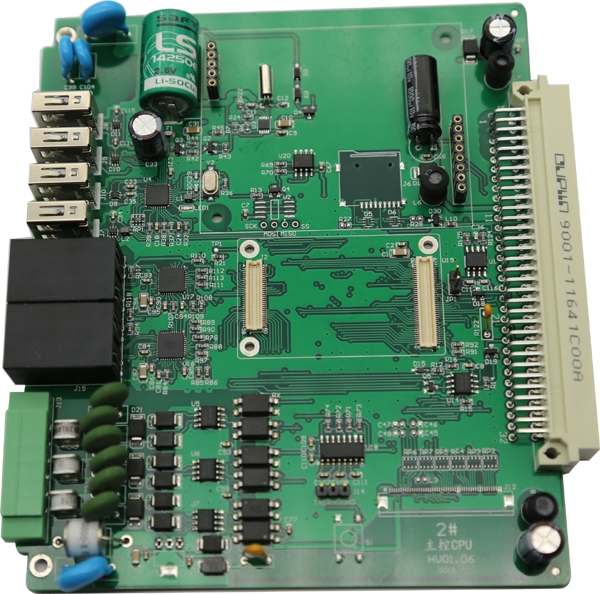
The components of circuit board and their basic functions:
Resistor:
A resistor is a tubular element that can reduce circuit voltage and current. And usually has special colored stripes on its outer surface. Its main purpose is to prevent excessive current entering the circuit area; according to the resistance rating of the component, each resistor can only stop a certain amount of current. The external stripes represent the resistance value that the assembler refers to when constructing the PCB. Improper placement of resistors can cause other circuit board components to damage the flow due to excessive current.
Capacitors:
It is a passive device. Usually use it in the power and electronics fields. It can store energy by maintaining an electric field. It consists of two parallel metal armors, usually use aluminum to make it, in which separate a dielectric material.
Diode:
These components are also called rectifiers because they perform the conversion from alternating current to pulsating direct current. Diodes are semiconductor mechanisms that act as unidirectional current switches, classified by type, voltage and current capacity.
Inductor or coil:
Inductors or coils are passive components that have the ability to store energy in the form of a magnetic field. They are made of a hollow coil head made of mainly two materials. And the conductor is made of enameled copper wire or enameled wire.
switch:
To locate the switch in an electronic circuit that controls the flow of current. It slows down the flow of electrons so that it is easy to switch it on/off. Their operation depends on whether they touch metal contacts, when they close and when they open.
fuse:
Fuses cut off the flow of electricity by burning the wires or metal pieces that make them up. It’s position in the the beginning of circuit. Thus if the current increases, it will reach the circuit and damage the device.
The working principle of the circuit board:
Use it to isolate the conductive layer of copper foil on the surface with the board-based insulating material. So that the current flows in various components along the pre-designed route to complete tasks. Such as work, amplification, attenuation, modulation, demodulation, and encoding and other functions.The internal design of the component forms a barrier against the flow of reverse current; this barrier is particularly helpful in protecting sensitive microchips, because these chips can easily fail due to excessive current.
